Published: 1972 | Southern Medical Journal, July 1972, Vol. 65, No 7
Humidification to reduce respiratory illnesses in nursery school children
Sale C
Abstract
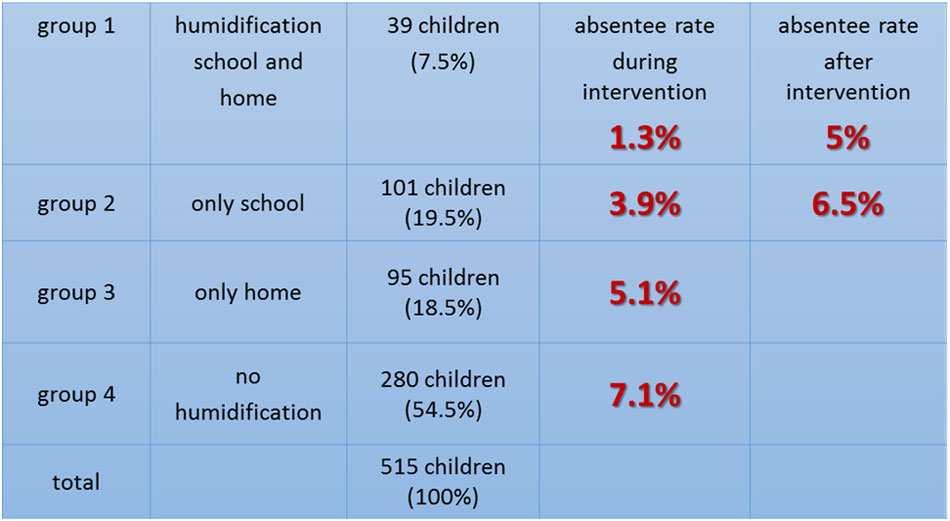
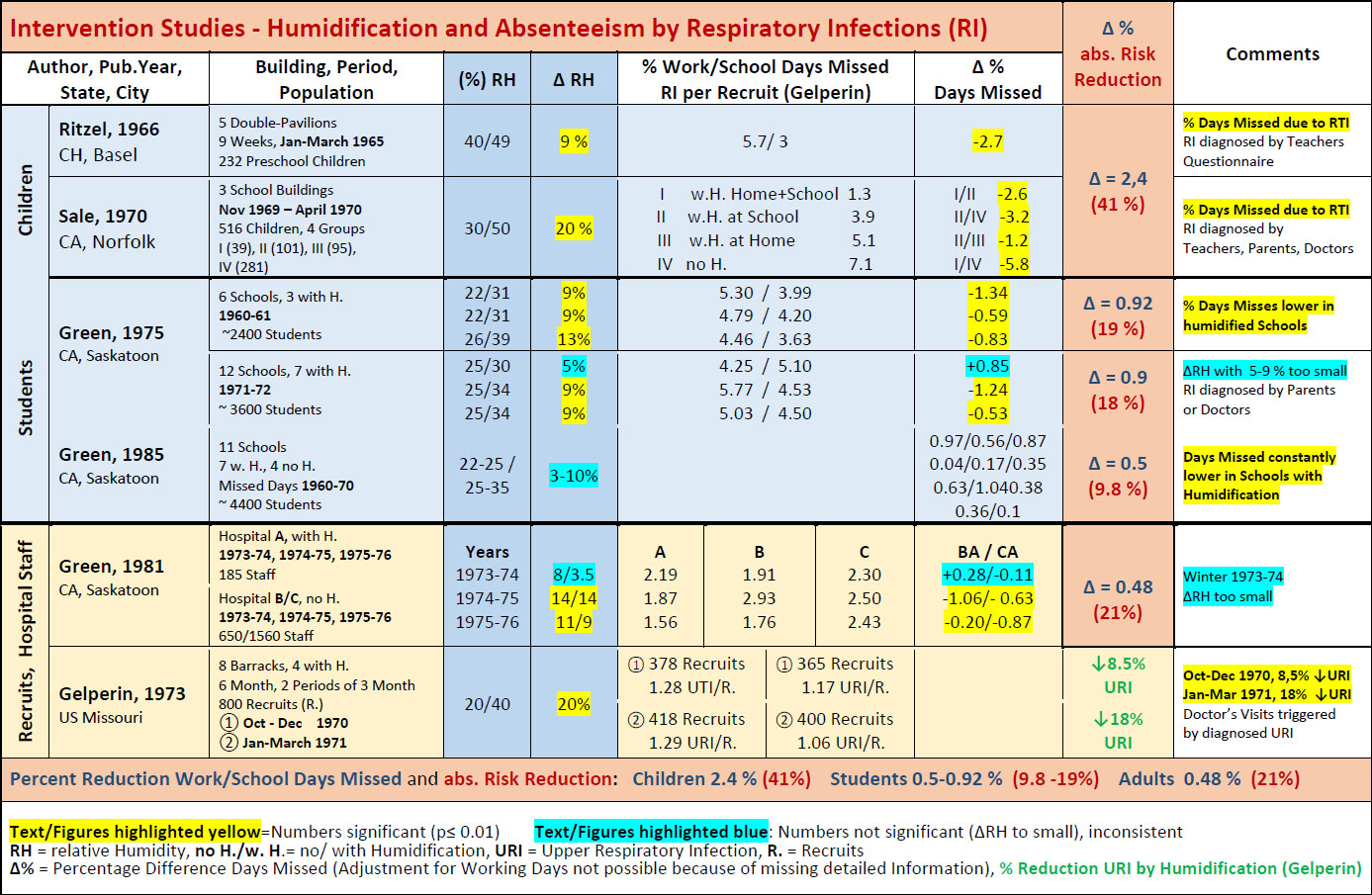
This prospective interventional study was done with 515 nursery children (2½ to 6 years old) in three private kindergarten buildings. The author analyzed the effects of four types of intervention: humidification in school and at home (group 1), only in school (group 2), only at home (group 3) and no humidification at all (group 4). Study period: Nov. 1969 to May 1970.
Sale analysed absentee days related to colds, identified by request on teachers, parents and care taking pediatrists. School building 1 was humidified with an average relative humidity of 50%, compared to the humidity of building 2 and 3, where humidity was 10 to 15% lower.
The data is summarized in the table.
Results: reduction of absentee days by almost 50% through humidification at school. A further decrease of absenteeism was achieved by additional humidification at home, while the absentee rates returned to pre-study rates after ending the humidification efforts.